Resizable arrays
Resizable arrays, also called dynamic arrays, dynamic tables, array lists and so on, are extensively used in many applications when the amount of data to be stored in the array is not known in advance or can change dynamically during the execution of the program.
For instance, the Scala code below reads all the words in a text file into a resizable array (Scala ArrayBuffer). This allows the words to be later processed in memory in the same order they appear in the file.
val words = collection.mutable.ArrayBuffer[String]()
val bufferedSource = io.Source.fromFile("test.txt")
for line <- bufferedSource.getLines do
for word <- line.trim.split(raw"\s+") if word != "" do
words += word
bufferedSource.close
Due to their importance in many applications, resizable arrays are implemented in many standard libraries:
ArrayBuffer in Scala
vector in the C++ standard library (NOTE: Vector in Scala is not a resizable array but a tree-based immutable collection data type)
java.util.ArrayList in Java
list in Python
Their main benefit of resizable arrays over fixed-size low-level arrays is that they allow amortized constant-time insertion and removal at the end. The benefit over mutable linked lists, that also allow constant time insertion and removal at the end, is that constant-time random access to the elements is supported and less memory allocations are performed. In general, memory allocations are not free but the runtime system must keep track of the free and allocated memory areas when objects are created and deleted. The plot below compares the performance of C++ vector (resizable array) and list (mutable linked list) when \(n\) elements are inserted at the end. These tests were run in an Ubuntu Linux machine with a 3.8GHz Intel Xeon W-2235 CPU.
The data structure and insertion at the end
The idea in resizable arrays is as follows: allocate a low-level array \(a\) with some extra space and maintain the following information.
The capacity \(c\), ie. the size, of the array \(a\). In Java and Scala, this is already included in the low-level array but in C++, for instance, raw arrays do not carry any additional information.
The size \(s\) of the resizable array, ie. the number of elements actually used in the underlying array \(a\). It always holds that \(s \le c\).
When an element is inserted at the end of the resizable array, we do the following:
If \(s < c\), we simply write the element in the index \(s\) of the array \(a\) and increase \(s\) by one.
If \(s = c\), we
allocate a new array of \(\alpha c\) elements, where \(\alpha > 1\) is an expansion factor constant (usually 1.5 or 2),
copy the \(s\) elements from the old array to the beginning of the new array, and
set the capacity to \(\alpha c\), insert the new element at index \(s\) in the new array and increase \(s\) by one.
Example: Inserting an element into a full resizable array
Consider the resizable array of integers shown below and suppose that we wish to insert the element 21 at the end of it.
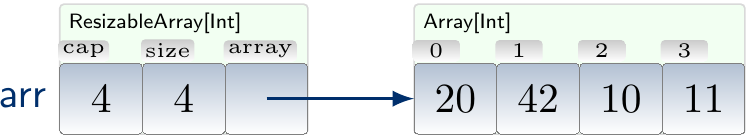
As the array was full, the insertion triggers expansion and results in the resizable array shown below.
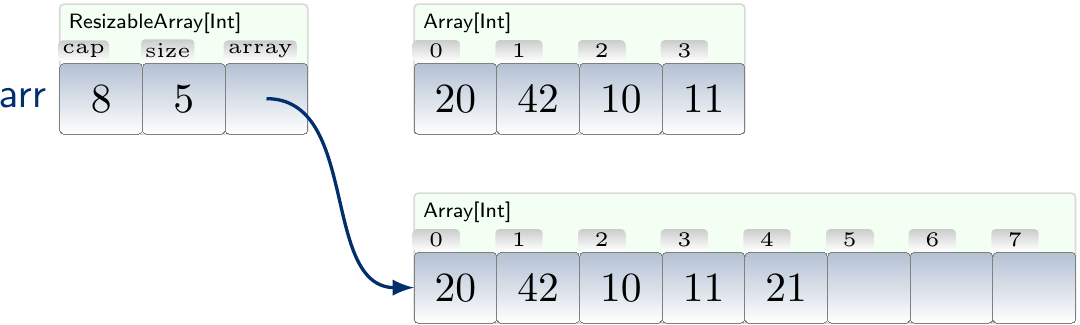
The old array will be deallocated by the runtime system in garbage-collected languages such as Java and Scala. In non-garbage collecting languages such as C++, the old array must be explicitly deallocated by the insertion operation code.
Example
The code below shows how appending elements in ArrayBuffer is implemented in the Scala version 2.11.8. The code is taken from the source code of ArrayBuffer and the source code of ResizableArray.
class ArrayBuffer[A](override protected val initialSize: Int)
extends AbstractBuffer[A]
with Buffer[A]
with GenericTraversableTemplate[A, ArrayBuffer]
with BufferLike[A, ArrayBuffer[A]]
with IndexedSeqOptimized[A, ArrayBuffer[A]]
with Builder[A, ArrayBuffer[A]]
with ResizableArray[A]
with CustomParallelizable[A, ParArray[A]]
with Serializable
{
// LINES REMOVED
/** Appends a single element to this buffer and returns
* the identity of the buffer. It takes constant amortized time.
*
* @param elem the element to append.
* @return the updated buffer.
*/
def +=(elem: A): this.type = {
ensureSize(size0 + 1)
array(size0) = elem.asInstanceOf[AnyRef]
size0 += 1
this
}
// LINES REMOVED
}
trait ResizableArray[A] extends IndexedSeq[A]
with GenericTraversableTemplate[A, ResizableArray]
with IndexedSeqOptimized[A, ResizableArray[A]]
{
override def companion: GenericCompanion[ResizableArray] = ResizableArray
protected def initialSize: Int = 16
protected var array: Array[AnyRef] = new Array[AnyRef](math.max(initialSize, 1))
protected var size0: Int = 0
// LINES REMOVED
/** Ensure that the internal array has at least `n` cells. */
protected def ensureSize(n: Int) {
// Use a Long to prevent overflows
val arrayLength: Long = array.length
if (n > arrayLength) {
var newSize: Long = arrayLength * 2
while (n > newSize)
newSize = newSize * 2
// Clamp newSize to Int.MaxValue
if (newSize > Int.MaxValue) newSize = Int.MaxValue
val newArray: Array[AnyRef] = new Array(newSize.toInt)
scala.compat.Platform.arraycopy(array, 0, newArray, 0, size0)
array = newArray
}
}
// LINES REMOVED
}
Analysis
Resizing the underlying array multiplies its capacity with the constant \(\alpha > 1\) and thus the new array sizes grow exponentially in the number of resize operations. However, in this way the resize operations also become more and more infrequent when the size of the array grows. And multiplying the size with a constant does not usually use too much extra memory either: if we only insert elements, then the array is always at least \(\frac{1}{\alpha}\)-full. For instance, when \(\alpha = 2\), we only “waste” at most the same amount of memory that we actually use for storing the elements.
Why do we multiply the size with a constant and not just add some non-neglible fixed number, say 1024, elements when resizing? The reason is that multiplying the size allows us to have amortized constant-time insertion of elements. That is, if we insert \(n\) elements in a resizable array, then
those insertions on which the resizing occurs are quite costly as memory allocation and copying must be done,
but the cumulative cost amortized to each insertion is constant. That is, performing \(n\) insertions takes \(\Oh{n}\) time.
Lets study the number of accesses done in each insertion (this is in linear correspondence to the running time). Suppose that (i) \(\alpha = 2\), (ii) we have inserted \(n\) elements in an empty array, and (iii) array resizing occurs when we insert the \(n+1\):th element. The number of extra array accesses when copying elements from an old array to the current new one in this and all the previous resizings is captured by the recurrence
where \(d\) is the initial size of the array. Thus
Adding the 1 normal array access per insertion, we get the amortized number of array accesses per insertion is at most \(\frac{2n+n}{n} = 3\).
Generally, for an arbitrary expansion factor \(\alpha > 1\), the extra cost is at most \(n \sum_{i=0}^\infty \frac{1}{\alpha^i} = n \frac{1}{1-\frac{1}{\alpha}} = n \frac{\alpha}{\alpha-1} = \Oh{n}\) and thus the amortized cost per insertion is a constant as well. As an example, when \(\alpha=1.1\), the amortized cost per insertion is at most \(11+1=12\) array accesses.
Example
For the expansion factor of 2, we can graphically illustrate the array accesses done when inserting \(9\) elements in a resizable array that initially has the capacity of \(1\) as follows:
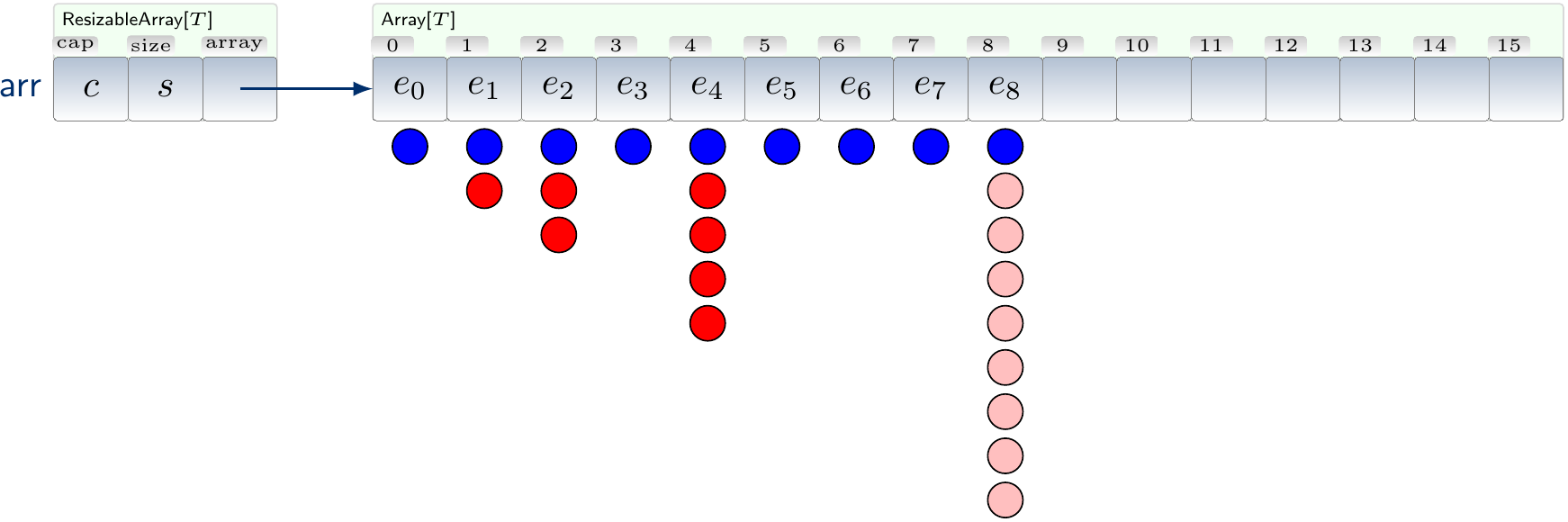
The blue dots are regular accesses when writing the new element, red ones are copy accesses from the previous expansions and the pink ones are the ones of the latest expansion. If we collapse the red towers right and the pink tower left, we get
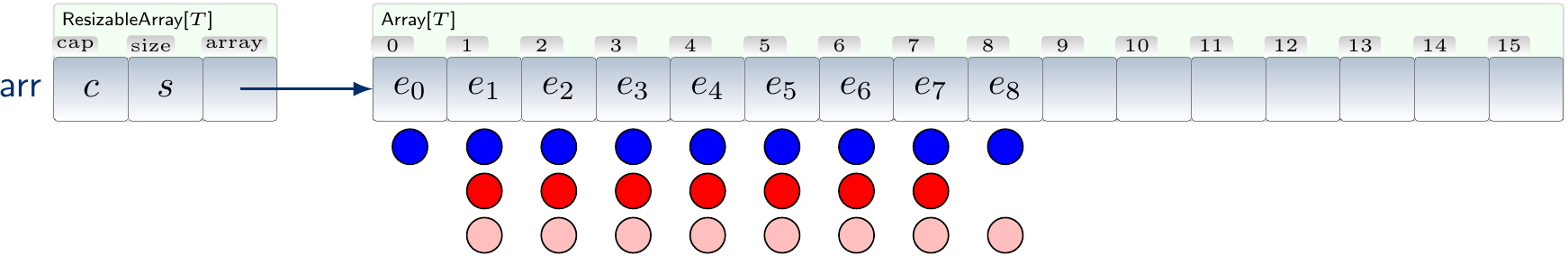
and see that each insert has at most 3 dots “amortized” to them.
Removing elements at the end
Removing the last element of a resizable array is easy as one only needs to decrease the index \(s\) by one (and, to enable timely garbage collection, replace the removed low-level array entry by the null pointer if the array elements are object references).
To avoid wasting too much memory, when should one contract the underlying low-level array? Again, the goal is to be able to perform both insertions and removals in amortized constant time. A working strategy is the following:
Define a lower bound constant \(0 < \beta < \frac{1}{\alpha}\).
If the load factor \(\frac{s}{c}\) is smaller than \(\beta\) after removing an element at the end, then allocate a new smaller low-level array of capacity \(\frac{c}{\alpha}\), copy the remaining element in it, and free the memory of the old low-level array.
The condition \(\beta < \frac{1}{\alpha}\) guarantees there are enough insertion and removal operations between the low-level array resizings so that the costs of the resizings can be amortized to the operations. Please refer to the Section 17.4 of Introduction to Algorithms (Aalto access) for an analysis of the case \(\alpha = 2\) and \(\beta = 0.25\).