Arrays
Arrays are a central built-in type in many programming languages such as Java, Scala, and C++. Here arrays are defined to mean “low-level arrays” that are fixed-sized sequences of elements of the same type, allocated in a continuous block of memory. In some programming languages, “arrays” can mean more sophisticated data structures, see the discussion at the end of this section.
In Java and Scala, elements in low-level arrays are either primitive types or references to objects residing in their own memory locations. Some other languages, such as C and C++, allow array elements to be structured objects as well.
Example
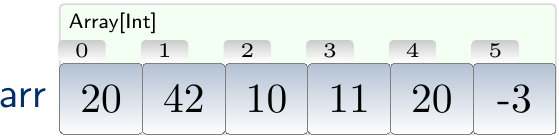
The figure below shown an object diagram for an array of integers.
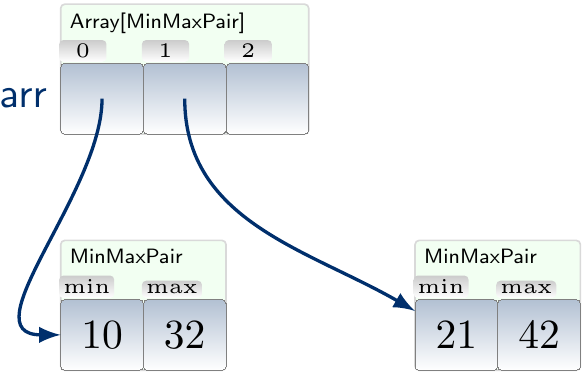
For an array of integer pair objects, the object diagram looks as following for Java and Scala. The third entry in the array on the right contains a null-reference not pointing to any object.
Properties of arrays:
Indexed access to elements (read and write), such as the expression
arr(i)in Scala, takes constant time. Searching for an element takes linear time in the worst case (unless, for instance, the array is sorted and one uses binary search).
Elements cannot be appended at the beginning or end. If this is desired, a new array with bigger size must be allocated and the array contents copied there together with the new element, which is a linear time operation. However, one can implement an extension of arrays in which insertions at the end take constant time on average — this this described in Section Resizable arrays.
In some higher-level interpreted languages, one has to use special libraries to access “low-level” arrays discussed above.
For instance, in Python neither list or array are low-level arrays but resizable array data types. If really needed, one can use the ctypes library to access low-level arrays.
Similarly, in JavaScript Arrays are not low-level arrays but allow resizing (appending at the end etc) and the data is not necessarily stored in a continuous block of memory. TypedArrays are closer to low-level arrays.